Create and configure geometric shapes programmatically using the Engine API—rectangles, ellipses, stars, polygons, lines, and custom vector paths combined with fills.
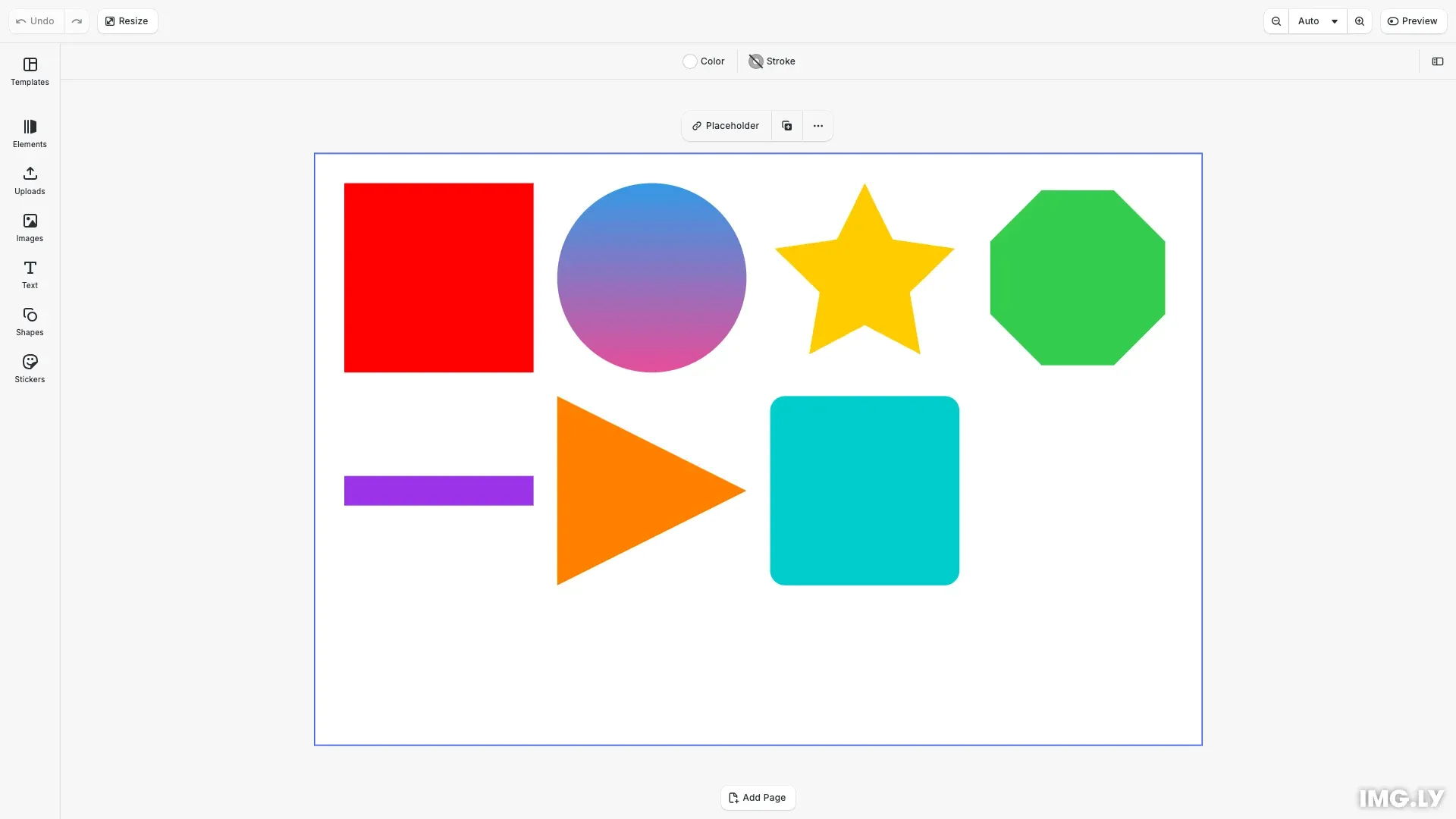
Understanding Shapes and Graphic Blocks#
What Are Shapes?#
Shapes in CE.SDK are geometric definitions—rectangles, ellipses, stars, and other forms—that exist as independent objects until attached to graphic blocks. We create shapes using type identifiers like 'rect' or 'ellipse', and they define the geometry while remaining invisible until combined with fills.
Shapes and fills are independent. Change a shape from a rectangle to a star while keeping the same fill, or change a fill from red to blue while maintaining the rectangular shape.
The Graphic Block System#
Graphic blocks serve as containers that bring shapes and fills together. When we create a graphic block, it starts empty—no shape, no fill, and therefore invisible. We then apply both a shape and a fill to make it appear on the canvas.
Here’s what a graphic block can hold:
- Shape: The geometric form (rectangle, ellipse, star, polygon, line, or vector path)
- Fill: The color, gradient, image, or video content that makes the shape visible
- Effects: Optional filters, blur, or shadows applied to the filled shape
- Transform: Position, rotation, and scale properties
Available Shape Types#
CE.SDK provides six built-in shape types:
- Rectangle (
'rect'): Basic rectangular shapes with optional rounded corners - Ellipse (
'ellipse'): Circular and oval shapes - Star (
'star'): Star shapes with configurable points and inner radius - Polygon (
'polygon'): Regular polygons with configurable number of sides - Line (
'line'): Straight lines spanning the block’s dimensions - Vector Path (
'vector_path'): Custom shapes using SVG path data
You can use short type names like 'rect' or fully qualified names like '//ly.img.ubq/shape/rect'—both work identically.
Checking Shape Support#
Before applying shapes, we verify that a block type supports them. Not all block types can have shapes—graphic blocks support shapes, but text blocks, scenes, and pages don’t.
const testGraphic = engine.block.create('graphic');engine.block.supportsShape(testGraphic); // Returns true
const testText = engine.block.create('text');engine.block.supportsShape(testText); // Returns false
engine.block.destroy(testText);engine.block.destroy(testGraphic);We always check supportsShape() to prevent errors when working with unknown or dynamic block types. Graphic blocks return true, while text blocks return false.
Creating Basic Shapes#
Creating a Rectangle#
We create a graphic block, apply a rectangle shape, and add a fill to make it visible:
const rectGraphic = engine.block.create('graphic');const rectShape = engine.block.createShape('rect');engine.block.setShape(rectGraphic, rectShape);
const redFill = engine.block.createFill('color');engine.block.setColor(redFill, 'fill/color/value', { r: 1.0, g: 0.0, b: 0.0, a: 1.0,});engine.block.setFill(rectGraphic, redFill);
engine.block.setWidth(rectGraphic, 64);engine.block.setHeight(rectGraphic, 64);engine.block.appendChild(page, rectGraphic);engine.block.setPositionX(rectGraphic, 10);engine.block.setPositionY(rectGraphic, 10);Shapes require fills to become visible. The shape defines the geometry while the fill provides the visual content.
Creating Other Shape Types#
Creating other shapes follows the same pattern with different shape types and properties.
Ellipse with gradient fill:
const ellipseGraphic = engine.block.create('graphic');const ellipseShape = engine.block.createShape('ellipse');engine.block.setShape(ellipseGraphic, ellipseShape);
const gradientFill = engine.block.createFill('gradient/linear');engine.block.setGradientColorStops(gradientFill, 'fill/gradient/colors', [ { color: { r: 0.2, g: 0.6, b: 0.9, a: 1.0 }, stop: 0.0 }, { color: { r: 0.9, g: 0.3, b: 0.6, a: 1.0 }, stop: 1.0 },]);engine.block.setFill(ellipseGraphic, gradientFill);
engine.block.setWidth(ellipseGraphic, 64);engine.block.setHeight(ellipseGraphic, 64);engine.block.appendChild(page, ellipseGraphic);engine.block.setPositionX(ellipseGraphic, 82);engine.block.setPositionY(ellipseGraphic, 10);Star with configurable points:
const starGraphic = engine.block.create('graphic');const starShape = engine.block.createShape('star');engine.block.setShape(starGraphic, starShape);
engine.block.setInt(starShape, 'shape/star/points', 5);engine.block.setFloat(starShape, 'shape/star/innerDiameter', 0.5);
const yellowFill = engine.block.createFill('color');engine.block.setColor(yellowFill, 'fill/color/value', { r: 1.0, g: 0.8, b: 0.0, a: 1.0,});engine.block.setFill(starGraphic, yellowFill);
engine.block.setWidth(starGraphic, 64);engine.block.setHeight(starGraphic, 64);engine.block.appendChild(page, starGraphic);engine.block.setPositionX(starGraphic, 154);engine.block.setPositionY(starGraphic, 10);Polygon with custom number of sides:
const polygonGraphic = engine.block.create('graphic');const polygonShape = engine.block.createShape('polygon');engine.block.setShape(polygonGraphic, polygonShape);
engine.block.setInt(polygonShape, 'shape/polygon/sides', 8);
const greenFill = engine.block.createFill('color');engine.block.setColor(greenFill, 'fill/color/value', { r: 0.2, g: 0.8, b: 0.3, a: 1.0,});engine.block.setFill(polygonGraphic, greenFill);
engine.block.setWidth(polygonGraphic, 64);engine.block.setHeight(polygonGraphic, 64);engine.block.appendChild(page, polygonGraphic);engine.block.setPositionX(polygonGraphic, 226);engine.block.setPositionY(polygonGraphic, 10);Line with stroke styling:
const lineGraphic = engine.block.create('graphic');const lineShape = engine.block.createShape('line');engine.block.setShape(lineGraphic, lineShape);
const purpleFill = engine.block.createFill('color');engine.block.setColor(purpleFill, 'fill/color/value', { r: 0.6, g: 0.2, b: 0.9, a: 1.0,});engine.block.setFill(lineGraphic, purpleFill);
engine.block.setWidth(lineGraphic, 64);engine.block.setHeight(lineGraphic, 10);engine.block.appendChild(page, lineGraphic);engine.block.setPositionX(lineGraphic, 10);engine.block.setPositionY(lineGraphic, 109);Configuring Shape Properties#
Discovering Properties#
Each shape type has unique properties that control its appearance. We discover these properties using findAllProperties():
// Discover what properties are available on a shapeconst exampleStarShape = engine.block.createShape('star');engine.block.findAllProperties(exampleStarShape);// Returns: ['shape/star/points', 'shape/star/innerDiameter', 'type', ...]engine.block.destroy(exampleStarShape);This shows what can be configured for each shape type.
Rectangle: Corner Radius#
Rectangles support independent corner radius values:
const roundedRectGraphic = engine.block.create('graphic');const roundedRectShape = engine.block.createShape('rect');engine.block.setShape(roundedRectGraphic, roundedRectShape);
engine.block.setFloat(roundedRectShape, 'shape/rect/cornerRadiusTL', 5.0);engine.block.setFloat(roundedRectShape, 'shape/rect/cornerRadiusTR', 5.0);engine.block.setFloat(roundedRectShape, 'shape/rect/cornerRadiusBL', 5.0);engine.block.setFloat(roundedRectShape, 'shape/rect/cornerRadiusBR', 5.0);
const cyanFill = engine.block.createFill('color');engine.block.setColor(cyanFill, 'fill/color/value', { r: 0.0, g: 0.8, b: 0.8, a: 1.0,});engine.block.setFill(roundedRectGraphic, cyanFill);
engine.block.setWidth(roundedRectGraphic, 64);engine.block.setHeight(roundedRectGraphic, 64);engine.block.appendChild(page, roundedRectGraphic);engine.block.setPositionX(roundedRectGraphic, 154);engine.block.setPositionY(roundedRectGraphic, 82);Set each corner independently using cornerRadiusTL, cornerRadiusTR, cornerRadiusBL, and cornerRadiusBR (values in pixels).
Star: Points and Inner Diameter#
Configure star shapes using two properties:
const starGraphic = engine.block.create('graphic');const starShape = engine.block.createShape('star');engine.block.setShape(starGraphic, starShape);
engine.block.setInt(starShape, 'shape/star/points', 5);engine.block.setFloat(starShape, 'shape/star/innerDiameter', 0.5);
const yellowFill = engine.block.createFill('color');engine.block.setColor(yellowFill, 'fill/color/value', { r: 1.0, g: 0.8, b: 0.0, a: 1.0,});engine.block.setFill(starGraphic, yellowFill);
engine.block.setWidth(starGraphic, 64);engine.block.setHeight(starGraphic, 64);engine.block.appendChild(page, starGraphic);engine.block.setPositionX(starGraphic, 154);engine.block.setPositionY(starGraphic, 10);The points property (minimum 3) sets the number of points. The innerDiameter (0.0 to 1.0) controls point sharpness.
Polygon: Number of Sides#
Configure polygons by setting the number of sides:
const polygonGraphic = engine.block.create('graphic');const polygonShape = engine.block.createShape('polygon');engine.block.setShape(polygonGraphic, polygonShape);
engine.block.setInt(polygonShape, 'shape/polygon/sides', 8);
const greenFill = engine.block.createFill('color');engine.block.setColor(greenFill, 'fill/color/value', { r: 0.2, g: 0.8, b: 0.3, a: 1.0,});engine.block.setFill(polygonGraphic, greenFill);
engine.block.setWidth(polygonGraphic, 64);engine.block.setHeight(polygonGraphic, 64);engine.block.appendChild(page, polygonGraphic);engine.block.setPositionX(polygonGraphic, 226);engine.block.setPositionY(polygonGraphic, 10);Vector Paths: Custom SVG Paths#
Create custom shapes using SVG path data:
const vectorPathGraphic = engine.block.create('graphic');const vectorPathShape = engine.block.createShape('vector_path');engine.block.setShape(vectorPathGraphic, vectorPathShape);
engine.block.setString( vectorPathShape, 'shape/vector_path/path', 'M 0,0 L 100,50 L 0,100 Z',);
const orangeFill = engine.block.createFill('color');engine.block.setColor(orangeFill, 'fill/color/value', { r: 1.0, g: 0.5, b: 0.0, a: 1.0,});engine.block.setFill(vectorPathGraphic, orangeFill);
engine.block.setWidth(vectorPathGraphic, 64);engine.block.setHeight(vectorPathGraphic, 64);engine.block.appendChild(page, vectorPathGraphic);engine.block.setPositionX(vectorPathGraphic, 82);engine.block.setPositionY(vectorPathGraphic, 82);Vector paths support single-path SVG data only. For complex multi-path graphics, use image fills with SVG files.
Combining Shapes with Fills#
Why Fills Matter#
Shapes define geometry but remain invisible without fills. Fills provide the visual content that makes shapes visible on the canvas.
Shape and Fill Independence#
Shapes and fills operate independently—change one without affecting the other. We can replace a shape while keeping its fill, or change a fill while maintaining the shape geometry. This enables flexible design workflows where shapes and fills can be modified separately.
For comprehensive fill system documentation, see the Fills Overview guide.
Managing Shapes#
Retrieving Shapes#
We can access the current shape on any graphic block:
// Get the shape ID from a graphic blockconst shapeId = engine.block.getShape(graphic);
// Check what type of shape it isconst shapeType = engine.block.getType(shapeId);// Returns: '//ly.img.ubq/shape/rect' or similarUse this pattern to inspect and modify existing shapes.
Replacing Shapes#
Replace shapes by applying the new shape first, then destroying the old one:
const oldShape = engine.block.getShape(graphic);const newShape = engine.block.createShape('ellipse');
engine.block.setShape(graphic, newShape);engine.block.destroy(oldShape);Always destroy old shapes after replacement to prevent memory leaks.
Positioning and Transforms#
Transforms apply to the graphic block. The shape geometry scales automatically:
const page = engine.block.findByType('page')[0];engine.block.appendChild(page, graphic);
engine.block.setPositionX(graphic, 100);engine.block.setPositionY(graphic, 100);engine.block.setRotation(graphic, Math.PI / 4);engine.block.setWidth(graphic, 200);engine.block.setHeight(graphic, 200);Troubleshooting#
Shape Not Visible#
If your shape doesn’t appear, verify these requirements:
Check fill is applied:
const fill = engine.block.getFill(graphic);if (!fill) { const colorFill = engine.block.createFill('color'); engine.block.setColor(colorFill, 'fill/color/value', { r: 1, g: 0, b: 0, a: 1 }); engine.block.setFill(graphic, colorFill);}Check dimensions:
const width = engine.block.getWidth(graphic);const height = engine.block.getHeight(graphic);if (width === 0 || height === 0) { engine.block.setWidth(graphic, 100); engine.block.setHeight(graphic, 100);}Check scene hierarchy:
const parent = engine.block.getParent(graphic);if (!parent) { const page = engine.block.findByType('page')[0]; engine.block.appendChild(page, graphic);}Cannot Apply Shape#
Verify the block type supports shapes:
if (!engine.block.supportsShape(blockId)) { console.error('This block type does not support shapes'); // Use a graphic block instead const graphic = engine.block.create('graphic');}Shape Properties Not Changing#
Use the correct setter method for each property type:
// Integer propertiesengine.block.setInt(shape, 'shape/polygon/sides', 5);
// Float propertiesengine.block.setFloat(shape, 'shape/star/innerDiameter', 0.5);
// String propertiesengine.block.setString(shape, 'shape/vector_path/path', 'M 0,0 L 100,100');List available properties first if you’re unsure:
const properties = engine.block.findAllProperties(shape);console.log('Available properties:', properties);API Reference#
| Method | Description | Returns |
|---|---|---|
block.create('graphic') | Create a new graphic block | Block ID (number) |
block.createShape(type) | Create shape of specified type | Shape ID (number) |
block.setShape(block, shape) | Apply shape to graphic block | void |
block.getShape(block) | Get shape attached to block | Shape ID (number) |
block.supportsShape(block) | Check if block supports shapes | boolean |
block.getType(shape) | Get shape type identifier | string |
block.findAllProperties(shape) | List available properties | string[] |
block.setInt(shape, prop, value) | Set integer property | void |
block.setFloat(shape, prop, value) | Set float property | void |
block.setString(shape, prop, value) | Set string property | void |
block.destroy(shape) | Destroy shape and free memory | void |