Crop images to focus on key subjects, remove unwanted elements, or prepare visuals for specific formats like social media or print using CE.SDK’s crop system.
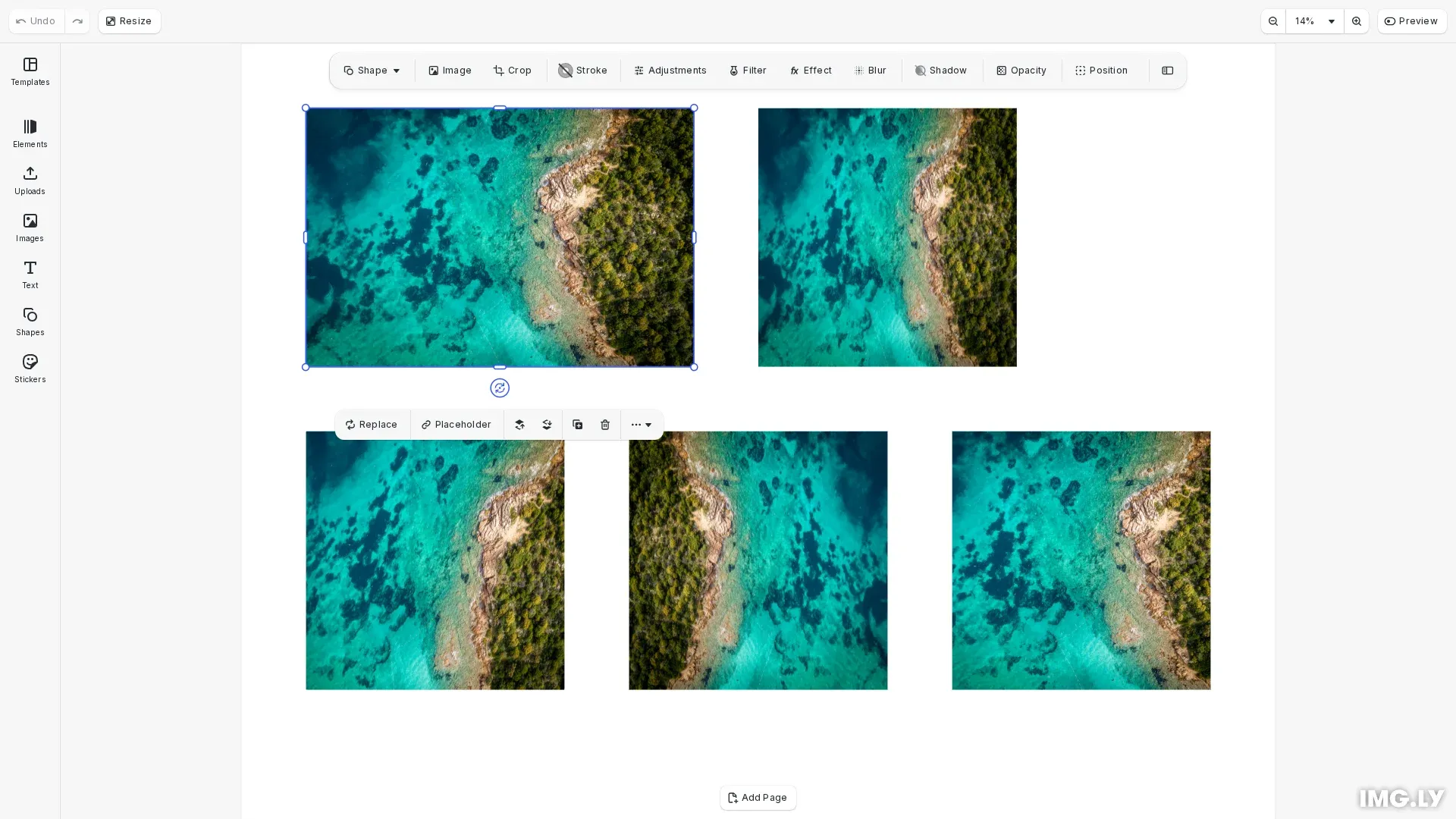
Image cropping in CreativeEditor SDK (CE.SDK) lets you select a region inside an image and discard everything outside that frame. Unlike resizing which changes overall dimensions uniformly, cropping removes unwanted areas while preserving original pixel quality in the selected region.
This guide covers both interactive cropping using the built-in UI and programmatic cropping using the engine API for automation workflows.
Using the Built-in Crop UI#
The CE.SDK default UI provides an interactive crop tool that allows users to visually adjust crop areas with real-time feedback.
User Workflow#
With the default UI configuration, users can crop images through a visual workflow:
- Select an image - Click on any image block in the canvas
- Enter crop mode - Double-click the image or click the crop icon in the toolbar
- Adjust the crop area - Drag corners or edges to resize the visible region
- Choose aspect ratio - Select a preset ratio if available (e.g., 1:1, 4:3, 16:9)
- Apply the crop - Click “Done” or press Enter to apply changes
The cropped image appears in your project, but the underlying original image preserves its values, even when you rotate or resize the cropped image.
Enable Crop Features in Custom UI#
For developers building custom UIs, you can enable crop functionality using editor settings:
// Enable double-click to enter crop modecesdk.editor.setSettingBool('doubleClickToCropEnabled', true);
// Show crop handles on the control gizmocesdk.editor.setSettingBool('controlGizmo/showCropHandles', true);
// Show crop scale handlescesdk.editor.setSettingBool('controlGizmo/showCropScaleHandles', true);Define Preset Aspect Ratios#
You can define available aspect ratios to guide user choices:
const aspectRatios = [ 'Free', // Unconstrained '1:1', // Square '4:5', // Instagram Portrait '16:9', // Widescreen 'Custom:3:2' // Custom ratios];cesdk.editor.setSettingString('ui/crop/aspectRatios', aspectRatios.join(','));Programmatic Cropping#
For automation, batch processing, or dynamic applications, you can control cropping entirely through the engine API.
Check Crop Support#
Before applying crop operations, verify the block supports cropping using engine.block.supportsCrop(). Graphic blocks with image fills support cropping:
// Verify the block supports cropping before applying crop operationsconst supportsCrop = engine.block.supportsCrop(imageBlock);console.log('Block supports crop:', supportsCrop);Content Fill Modes#
CE.SDK provides three content fill modes that control how images fit within their frame. Set the mode using engine.block.setContentFillMode():
// Check if the block supports content fill modesconst supportsFillMode = engine.block.supportsContentFillMode(imageBlock);console.log('Supports content fill mode:', supportsFillMode);
// Get the current content fill modeconst currentMode = engine.block.getContentFillMode(imageBlock);console.log('Current fill mode:', currentMode);
// Set content fill mode - options are 'Crop', 'Cover', 'Contain'// 'Cover' automatically scales and positions to fill the entire frameengine.block.setContentFillMode(imageBlock, 'Cover');The available modes are:
- Crop - Manual control over the exact crop region using scale, translation, and rotation
- Cover - Automatically scale and position content to fill the entire frame (no empty areas)
- Contain - Automatically scale and position content to fit entirely within the frame (may show background)
Scale Crop#
Scale the image content within its frame using crop scale APIs. Values greater than 1.0 zoom in, values less than 1.0 zoom out:
// Create another image block to demonstrate crop scalingconst scaleBlock = await engine.block.addImage(imageUri, { size: { width: 200, height: 200 }});engine.block.appendChild(page, scaleBlock);engine.block.setPositionX(scaleBlock, 400);engine.block.setPositionY(scaleBlock, 50);
// Set content fill mode to 'Crop' for manual controlengine.block.setContentFillMode(scaleBlock, 'Crop');
// Scale the content within the crop frame// Values > 1 zoom in, values < 1 zoom outengine.block.setCropScaleX(scaleBlock, 1.5);engine.block.setCropScaleY(scaleBlock, 1.5);
// Or use uniform scaling from centerengine.block.setCropScaleRatio(scaleBlock, 1.2);
// Get the current scale valuesconst scaleX = engine.block.getCropScaleX(scaleBlock);const scaleY = engine.block.getCropScaleY(scaleBlock);const scaleRatio = engine.block.getCropScaleRatio(scaleBlock);console.log('Crop scale:', { scaleX, scaleY, scaleRatio });Use setCropScaleRatio() for uniform scaling from the center, or setCropScaleX() and setCropScaleY() for non-uniform scaling.
Translate Crop#
Pan the image content within the crop frame using translation. Values are percentages of the crop frame dimensions:
// Pan the content within the crop frame using translation// Values are in percentage of the crop frame dimensionsengine.block.setCropTranslationX(scaleBlock, 0.1); // Move 10% rightengine.block.setCropTranslationY(scaleBlock, -0.1); // Move 10% up
// Get the current translation valuesconst translationX = engine.block.getCropTranslationX(scaleBlock);const translationY = engine.block.getCropTranslationY(scaleBlock);console.log('Crop translation:', { translationX, translationY });Positive X moves content right, positive Y moves content down.
Fill Frame#
Adjust the crop to ensure content fills the frame without empty areas using engine.block.adjustCropToFillFrame(). The minScaleRatio parameter sets the minimum allowed scale:
// Ensure content covers the entire frame without gaps// The minScaleRatio parameter sets the minimum scale allowedconst adjustedRatio = engine.block.adjustCropToFillFrame(scaleBlock, 1.0);console.log('Adjusted scale ratio:', adjustedRatio);This is useful after applying translations or rotations that might reveal empty areas.
Rotate Crop#
Rotate the image content within its frame using engine.block.setCropRotation(). Rotation is specified in radians:
// Create an image block to demonstrate crop rotationconst rotateBlock = await engine.block.addImage(imageUri, { size: { width: 200, height: 200 }});engine.block.appendChild(page, rotateBlock);engine.block.setPositionX(rotateBlock, 50);engine.block.setPositionY(rotateBlock, 300);engine.block.setContentFillMode(rotateBlock, 'Crop');
// Rotate the content within the crop frame (in radians)// Math.PI / 4 = 45 degreesengine.block.setCropRotation(rotateBlock, Math.PI / 12);
// Get the current rotationconst rotation = engine.block.getCropRotation(rotateBlock);console.log('Crop rotation (radians):', rotation);
// Ensure content still fills the frame after rotationengine.block.adjustCropToFillFrame(rotateBlock, 1.0);After rotation, call adjustCropToFillFrame() to ensure content still covers the frame.
Flip Crop#
Flip the image content horizontally or vertically within its crop frame. This flips the content itself, not the block:
// Create an image block to demonstrate flippingconst flipBlock = await engine.block.addImage(imageUri, { size: { width: 200, height: 200 }});engine.block.appendChild(page, flipBlock);engine.block.setPositionX(flipBlock, 300);engine.block.setPositionY(flipBlock, 300);engine.block.setContentFillMode(flipBlock, 'Crop');
// Flip the content horizontallyengine.block.flipCropHorizontal(flipBlock);Lock Aspect Ratio#
Lock the crop aspect ratio during interactive editing using engine.block.setCropAspectRatioLocked(). When locked, crop handles maintain the current aspect ratio:
// Create an image block to demonstrate aspect ratio lockingconst lockBlock = await engine.block.addImage(imageUri, { size: { width: 200, height: 200 }});engine.block.appendChild(page, lockBlock);engine.block.setPositionX(lockBlock, 550);engine.block.setPositionY(lockBlock, 300);engine.block.setContentFillMode(lockBlock, 'Crop');
// Lock the crop aspect ratio - when locked, crop handles maintain// the current aspect ratio during resize operationsengine.block.setCropAspectRatioLocked(lockBlock, true);
// Check if aspect ratio is lockedconst isLocked = engine.block.isCropAspectRatioLocked(lockBlock);console.log('Aspect ratio locked:', isLocked);Reset Crop#
Reset all crop transformations to their default state using engine.block.resetCrop():
// Reset crop to default state (sets content fill mode to 'Cover')engine.block.resetCrop(lockBlock);Coordinate System#
Crop transforms use normalized values:
| Property | Value Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Scale | Float (0.0+) | 1.0 is original size, 2.0 is double, 0.5 is half |
| Translation | Float (-1.0 to 1.0) | Percentage of frame dimensions |
| Rotation | Float (radians) | Math.PI = 180°, Math.PI/2 = 90° |
All crop values are independent of canvas zoom level.
Combining Crop with Other Transforms#
You can combine crop operations with other block transforms like position, rotation, and scale. Crop transforms affect the content within the block, while block transforms affect the block itself on the canvas:
// Crop the content (scales/pans the image within its frame)engine.block.setCropScaleRatio(imageBlock, 1.5);engine.block.setCropRotation(imageBlock, Math.PI / 12);
// Transform the block itself (moves/rotates the entire block on canvas)engine.block.setRotation(imageBlock, Math.PI / 6);engine.block.setWidth(imageBlock, 400);Troubleshooting#
| Issue | Cause / Fix |
|---|---|
| Crop functions throw error | Verify block supports crop with supportsCrop() |
| Black bars after scaling | Call adjustCropToFillFrame() or increase scale ratio |
| Content not filling frame | Check content fill mode - use ‘Cover’ for automatic fill |
| Unexpected crop behavior | Ensure content fill mode is set to ‘Crop’ for manual control |
| Crop handles not visible in UI | Enable with cesdk.editor.setSettingBool('controlGizmo/showCropHandles', true) |
API Reference#
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
block.supportsCrop(id) | Check if a block supports cropping |
block.supportsContentFillMode(id) | Check if block supports fill modes |
block.setContentFillMode(id, mode) | Set content fill mode (Crop, Cover, Contain) |
block.getContentFillMode(id) | Get current content fill mode |
block.setCropScaleRatio(id, ratio) | Set uniform crop scale from center |
block.setCropScaleX(id, scaleX) | Set horizontal crop scale |
block.setCropScaleY(id, scaleY) | Set vertical crop scale |
block.setCropTranslationX(id, x) | Set horizontal crop translation |
block.setCropTranslationY(id, y) | Set vertical crop translation |
block.setCropRotation(id, rotation) | Set crop rotation in radians |
block.getCropScaleRatio(id) | Get uniform crop scale ratio |
block.getCropScaleX(id) | Get horizontal crop scale |
block.getCropScaleY(id) | Get vertical crop scale |
block.getCropTranslationX(id) | Get horizontal crop translation |
block.getCropTranslationY(id) | Get vertical crop translation |
block.getCropRotation(id) | Get crop rotation in radians |
block.adjustCropToFillFrame(id, minRatio) | Adjust crop to fill frame |
block.flipCropHorizontal(id) | Flip content horizontally |
block.flipCropVertical(id) | Flip content vertically |
block.setCropAspectRatioLocked(id, locked) | Lock/unlock aspect ratio |
block.isCropAspectRatioLocked(id) | Check if aspect ratio is locked |
block.resetCrop(id) | Reset crop to default state |