This guide shows how to scale videos using CE.SDK in your Android app. You’ll learn how to scale video blocks proportionally, scale groups, and apply scaling constraints to protect template structure.
What you’ll learn#
- Scale videos programmatically using Kotlin
- Scale proportionally or non-uniformly
- Scale grouped elements
- Apply scale constraints in templates
When to use#
Use scaling to:
- Emphasize or de-emphasize elements
- Fit videos to available space without cropping
- Enable pinch-to-zoom gestures or dynamic layouts
Scale a video uniformly#
Scaling uses the scale(block: DesignBlock, scaleX: Float, scaleY: Float, anchorX: Float = 0f, anchorY: Float = 0f) function. A scale value of 1.0f is the original scale. Values larger than 1.0f increase the scale of the block and values lower than 1.0f scale the block smaller. A value of 2.0f, for example makes the block twice as large.
The following code scales the video to 150% of its original size. The origin anchor point remains unchanged, so the video expands down and to the right:
engine.block.scale(videoBlock, 1.5f, 1.5f)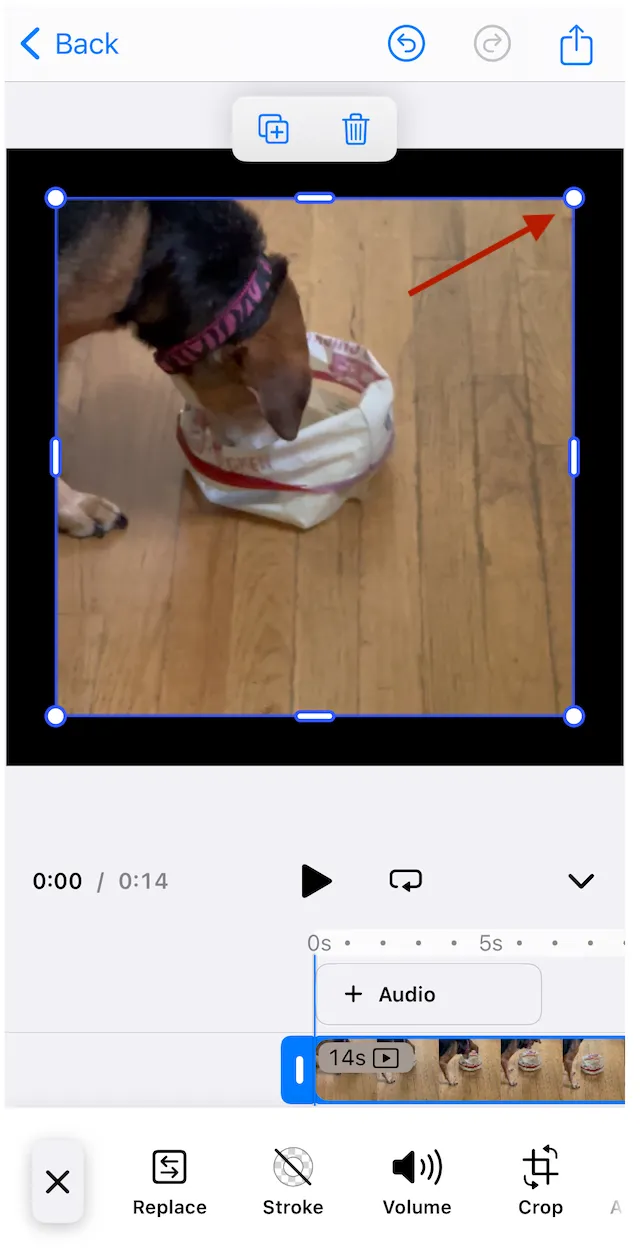
By default, the anchor point for the video when scaling is the origin point on the top left. The scale function has optional parameters to move the anchor point in the x and y direction. They can have values between 0.0f and 1.0f
The following code scales the video to 150% of its original size. The origin anchor point is 0.5, 0.5, so the video expands from the center:
engine.block.scale(videoBlock, 1.5f, 1.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f)
Scale non-uniformly#
To stretch or compress only one axis, thus distorting a video, use the crop scale function in combination with the width or height function. How you decide to make the adjustment will have different results. Below are three examples of scaling the original video in the x direction only.

import ly.img.engine.SizeMode
engine.block.setWidthMode(videoBlock, SizeMode.AUTO)val newWidth = engine.block.getWidth(videoBlock) * 1.5fengine.block.setWidth(videoBlock, newWidth)The preceding code adjusts the width of the block and allows the engine to adjust the scale of the video to maintain it as a fill.
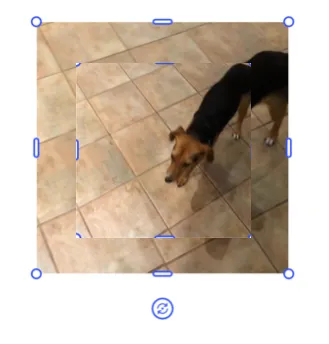
engine.block.setCropScaleX(videoBlock, 1.5f)engine.block.setWidthMode(videoBlock, SizeMode.AUTO)val newWidth = engine.block.getWidth(videoBlock) * 1.5fengine.block.setWidth(videoBlock, newWidth)The preceding code uses crop scale to scale the video in a single direction and then adjusts the block’s width to match the change. The change in width does not take the crop into account and so distorts the video as it’s scaling the scaled video.
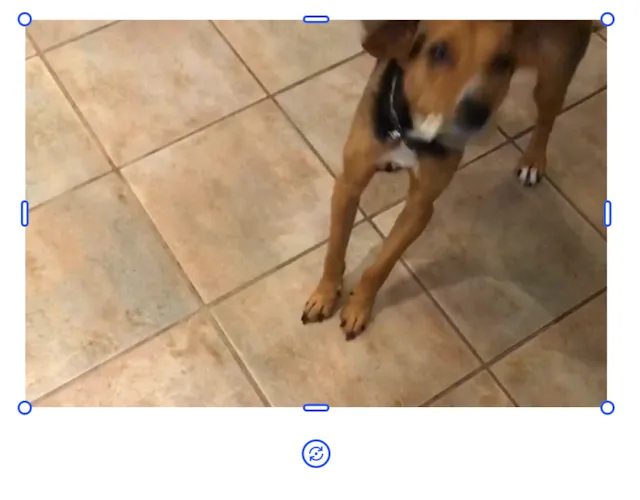
engine.block.setCropScaleX(videoBlock, 1.5f)engine.block.setWidthMode(videoBlock, SizeMode.AUTO)val newWidth = engine.block.getWidth(videoBlock) * 1.5fengine.block.setWidth(videoBlock, newWidth, true) // maintainCrop = trueBy setting the maintainCrop parameter to true, expanding the width of the video by the scale factor respects the crop scale and the video is less distorted.
Scale multiple elements together#
Group blocks to scale them proportionally:
val groupId = engine.block.group(listOf(videoBlock, textBlock))engine.block.scale(groupId, 0.75f, 0.75f)The preceding code scales the entire group to 75%.
Lock scaling#
When working with templates, you can lock a block from scaling by setting its scope. Remember that the global layer has to defer to the blocks using setGlobalScope.
engine.block.setScopeEnabled(videoBlock, "layer/resize", false)To prevent users from transforming an element at all:
engine.block.setTransformLocked(videoBlock, true)