The CreativeEditor SDK (CE.SDK) offers both interactive UI components and powerful Kotlin APIs for cropping images. Image cropping is an essential feature for any Android photo editing app, allowing users to focus on important content and fit images to specific dimensions. Whether you need simple aspect ratio adjustments or advanced programmatic, follow this guide to learn how to integrate cropping into your Android app.
Interactive crop interface#
The SDK includes ready-to-use crop controls that integrate seamlessly with your Android app. These components:
- Handle tap gestures and aspect ratio selection.
- Provide immediate visual feedback to users.
This is particularly useful for:
- Apps targeting social media formats.
- Maintaining consistent visual branding.
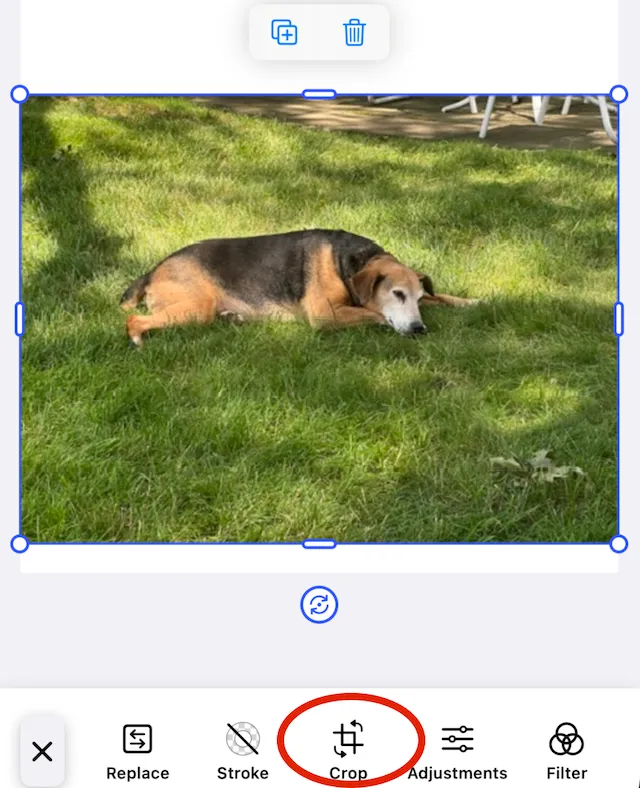
How users interact with crop tools#
- Tap the image to select it for editing.
- Tap the crop button in your app’s editing interface.
- Drag handles at corners and edges to define the crop region.
- Apply transformations like flip or rotate before finalizing.
- Confirm changes to complete the crop operation.
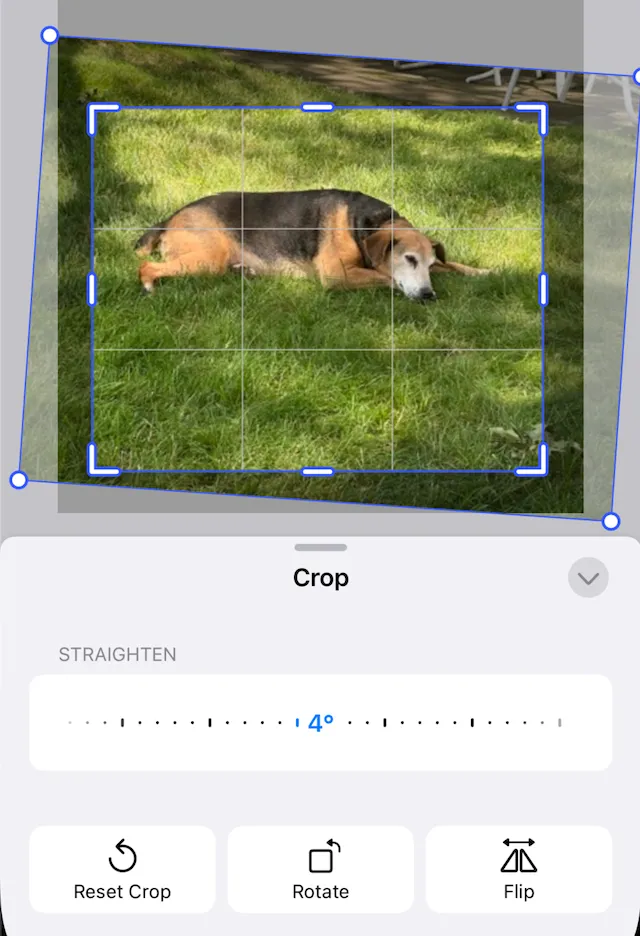
Once cropped, your image:
- Updates in the editor.
- Preserves the original data and transformation history for future adjustments.
Configuring crop capabilities#
By default, cropping is enabled in the editor UI. When building custom interfaces or specialized editing flows, you can control crop availability through configuration settings:
engine.editor.setSettingBoolean("doubleClickToCropEnabled", true)engine.editor.setSettingBoolean("controlGizmo/showCropHandles", true)engine.editor.setSettingBoolean("controlGizmo/showCropScaleHandles", true)The cropping handles are only available when a selected block has a fill of type FillType.Image. Otherwise setting the edit mode of the engine.editor to crop has no effect.
Crop images with Kotlin code#
For advanced Android applications, you’ll often need precise control over cropping operations through code. This approach suits very well:
- Batch processing
- Automated workflows
- Custom editing interfaces implementations.
The SDK automatically handles image fitting when you load content into blocks – if your image dimensions don’t match the container, intelligent cropping is applied automatically.
When implementing crop operations in your Kotlin code, keep in mind that you’re manipulating the underlying image’s scale, position, and orientation properties. The examples shown typically modify both x and y axes uniformly, but you can adjust them independently for creative distortion effects.
Reset Crop#
When an image is initially placed into a block it will get crop scale and crop translation values. Resetting the crop will return the image to the original values.
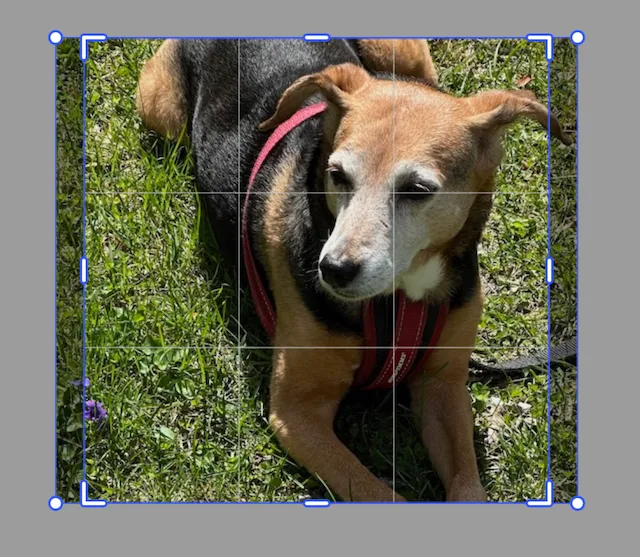

This is a block (called imageBlock in the example code) with the following elements:
- Dimensions of 400 × 400.
- Filled with an image that has dimensions of 600 × 530.
- The image has slight scaling and translation applied so that it fills the block evenly.
At any time, the code can execute the reset crop command to return it to this stage.
engine.block.resetCrop(imageBlock)Crop Translation#
The translation values:
- Adjust the placement of the origin point of an image.
- Can be read and changed.
- Aren’t pixel units or centimeters, but are scaled percentages.
An image that has its origin point at the origin point of the crop block will have a translation value of 0.0 for x and y.

engine.block.setCropTranslationX(imageBlock, 0.25f)This image:
- Has had its translation in the x direction set to 0.25.
- Was moved 1/4 of its width to the right as a result.
Setting the value to -0.25 would shift the origin to the left.
These are absolute values. Setting the x value to 0.25 and then setting it to -0.25 does not move the image to an offset of 0.0.
How values might affect the image:
setCropTranslationY(block: DesignBlock, translationY: Float)function adjusts the translation of the image in the vertical direction.- Negative values move the image up.
- Positive values move the image down.
To read the current crop translation values you can use the convenience getters for the x and y values.
val currentX = engine.block.getCropTranslationX(imageBlock)val currentY = engine.block.getCropTranslationY(imageBlock)Crop Scale#
The scale values:
- Adjust the height and width of the underlying image.
- Make the image larger when greater than 1.0.
- Make the image smaller when less than 1.0.
Unless the image also has offsetting translation applied, the center of the image will move.
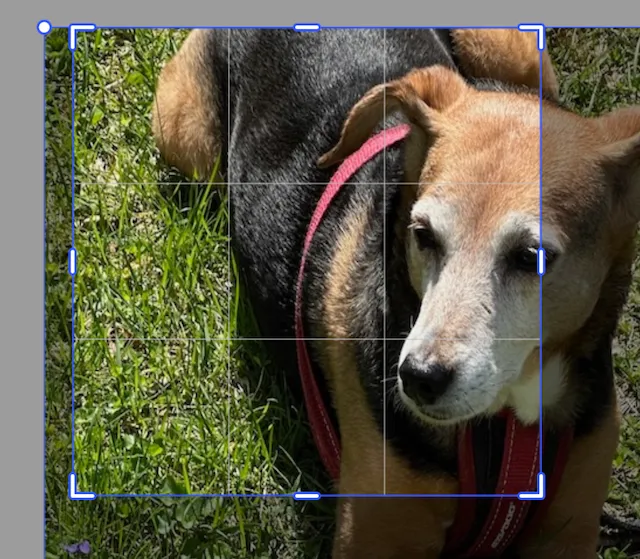
This image has been scaled by 1.5 in the x and y directions, but the origin point has not been translated. So, the center of the image has moved.
engine.block.setCropScaleX(imageBlock, 1.5f)engine.block.setCropScaleY(imageBlock, 1.5f)To read the current crop scale values you can use the convenience getters for the x and y values.
val currentX = engine.block.getCropScaleX(imageBlock)val currentY = engine.block.getCropScaleY(imageBlock)Crop Rotate#
Similar to rotating blocks, the crop rotation function uses radians in the following way:
- Positive values rotate clockwise.
- Negative values rotate counterclockwise.
- The image rotates around its center.
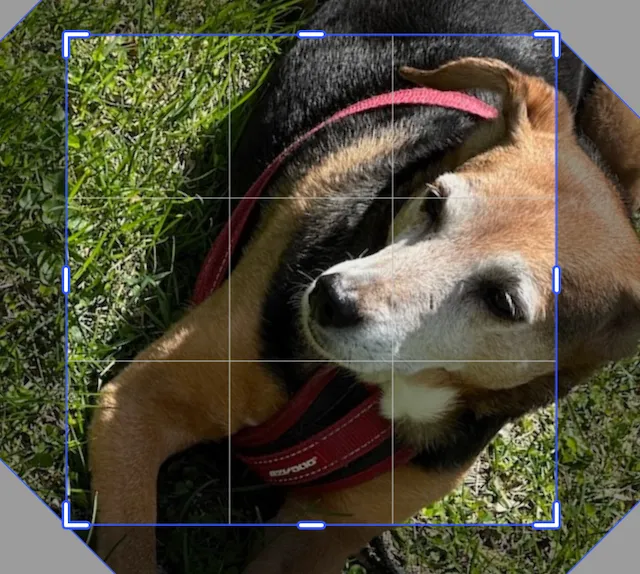
import kotlin.math.PI
engine.block.setCropRotation(imageBlock, (PI / 4.0).toFloat())For working with radians, Kotlin has a constant defined for pi. It can be used as PI from kotlin.math.PI. Because the setCropRotation function takes a Float for the rotation value, you can use .toFloat() to convert the Double to Float.
Crop to Scale Ratio#
To center crop an image, you can use the scale ratio. This will adjust the x and y scales of the image evenly, and adjust the translation to keep it centered.
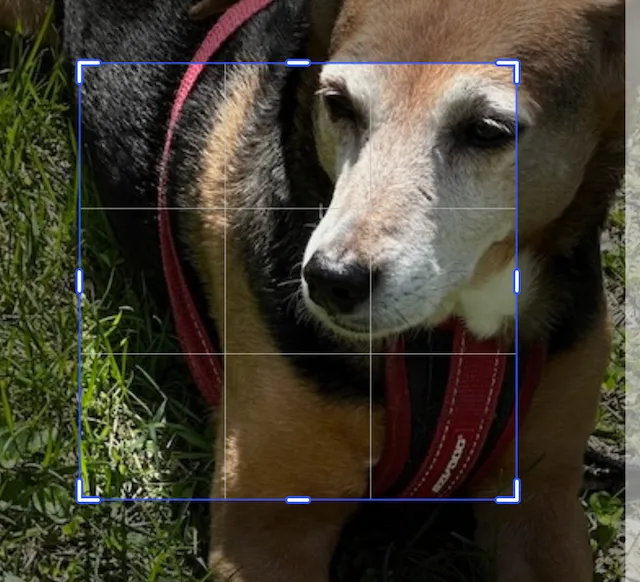
This image has been scaled by 2.0 in the x and y directions. Its translation has been adjusted by -0.5 in the x and y directions to keep the image centered.
engine.block.setCropScaleRatio(imageBlock, 2.0f)Using the crop scale ratio function is the same as calling the translation and scale functions, but in one line.
engine.block.setCropScaleX(imageBlock, 2.0f)engine.block.setCropScaleY(imageBlock, 2.0f)engine.block.setCropTranslationX(imageBlock, -0.5f)engine.block.setCropTranslationY(imageBlock, -0.5f)Chained Crops#
Crop operations can be chained together. The order of the chaining impacts the final image.
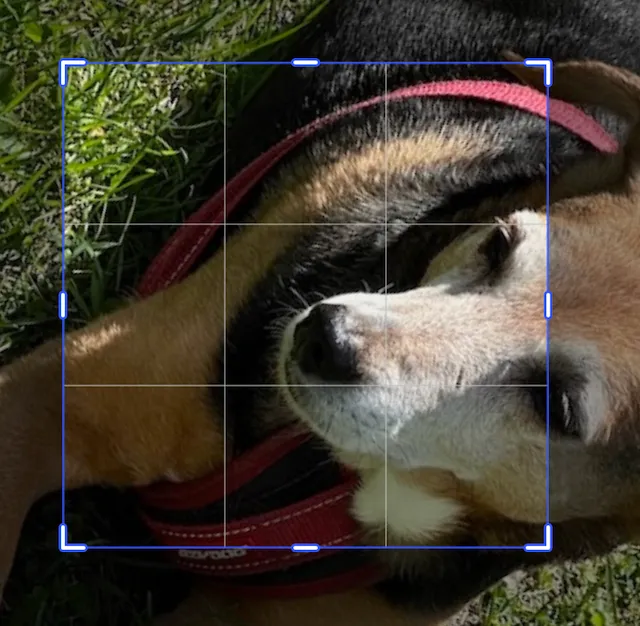
import kotlin.math.PI
engine.block.setCropScaleRatio(imageBlock, 2.0f)engine.block.setCropRotation(imageBlock, (PI / 3.0).toFloat())
import kotlin.math.PI
engine.block.setCropRotation(imageBlock, (PI / 3.0).toFloat())engine.block.setCropScaleRatio(imageBlock, 2.0f)Flipping the Crop#
There are two functions for crop flipping the image:
- Horizontal
- Vertical
They each flip the image along its center.
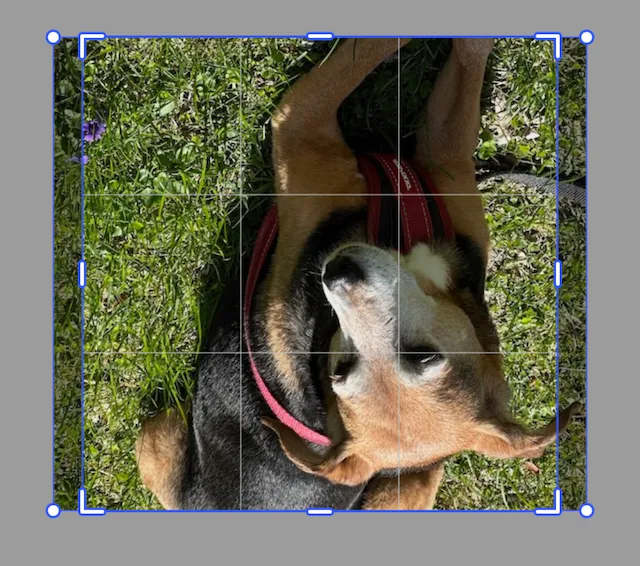

engine.block.flipCropVertical(imageBlock)engine.block.flipCropHorizontal(imageBlock)The image will be crop flipped every time the function gets called. So calling the function an even number of times will return the image to its original orientation.
Filling the Frame#
When the various crop operations cause the background of the crop block to be displayed, such as in the Crop Translation example above, the function
engine.block.adjustCropToFillFrame(imageBlock, minScaleRatio = 1.0f)will adjust the translation values and the scale values of the image so that the entire crop block is filled. This is not the same as resetting the crop.